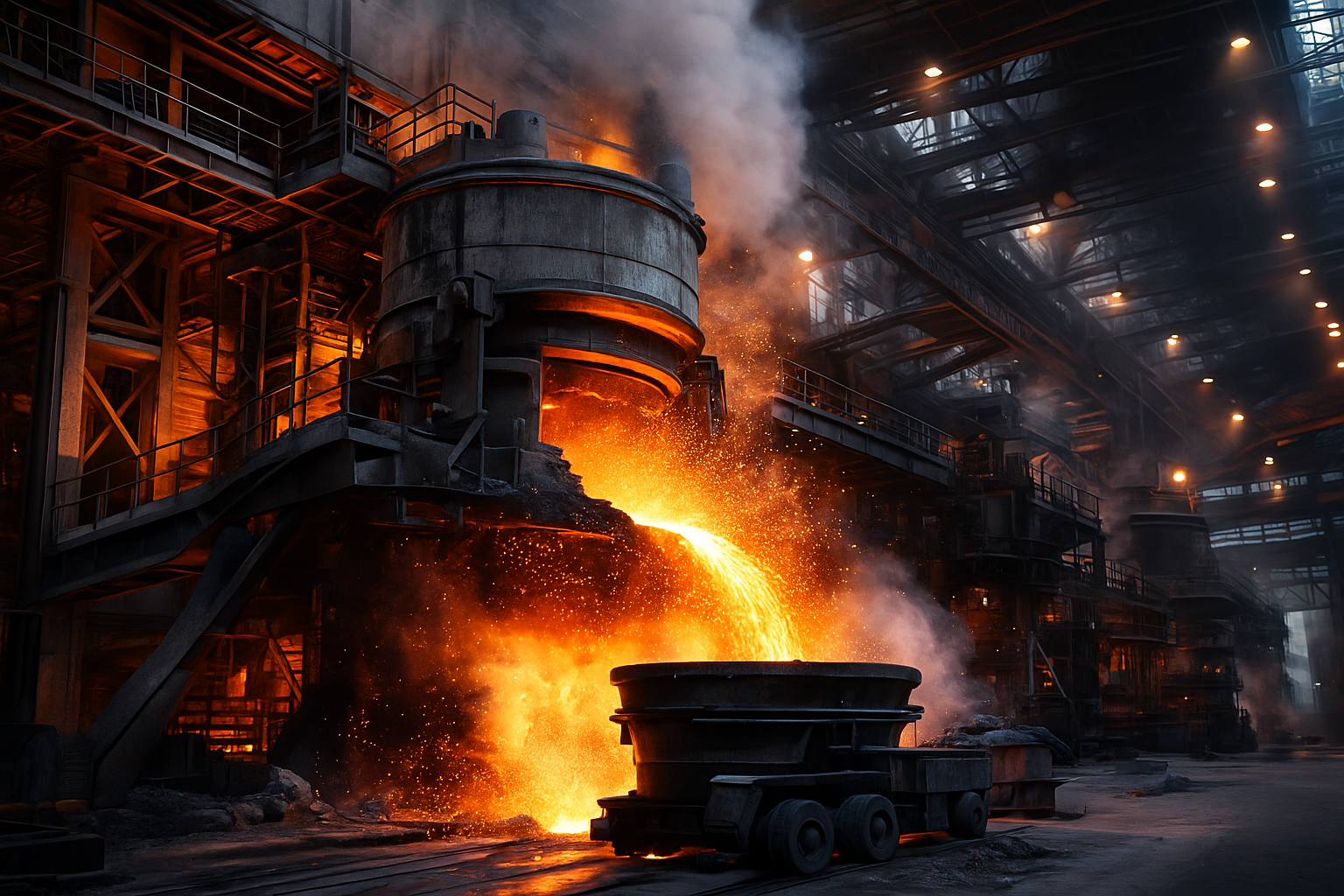
Steelmaking is a foundational industry—complex, energy-intensive, and ripe for innovation. Today, quantum technologies are moving from theory to practical deployment in this space, offering unprecedented capabilities in sensing, optimization, and materials science. From upstream mining to downstream smelting and quality control, quantum computing and quantum sensing are emerging as transformative tools.
Why Steelmaking Needs Quantum Innovation
The steel industry faces significant challenges: global decarbonization pressures, volatile supply chains, material efficiency demands, and aging infrastructure. Conventional digital technologies—AI, automation, and data analytics—have advanced operational control. But quantum technologies unlock an entirely new level of resolution and computational power.
Quantum computing can solve combinatorially complex problems classical computers struggle with, such as production scheduling and alloy design. Quantum sensing, on the other hand, enables ultra-precise measurements of gas composition, structural stress, and subsurface geology—critical for quality control, furnace optimization, and resource exploration.
Quantum Sensing: Enhanced Monitoring and Precision
Real-Time Furnace and Emissions Monitoring
Quantum cascade laser (QCL) sensors, now commercially available, provide ultra-sensitive and selective measurement of gases like CO and CO₂ inside high-temperature blast furnaces. These sensors help steelmakers finely tune combustion efficiency and cut emissions in real time.
Defect Detection and Quality Assurance
Quantum magnetometers, such as those using nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamond, are being tested to non-destructively map microscopic defects in finished steel components. These sensors can detect micro-cracks, internal stresses, and material fatigue far earlier than conventional tools.
Smart Mining and Exploration
Portable quantum gravimeters and magnetic sensors are being piloted by mining giants like BHP to map underground mineral formations. These technologies offer more accurate ore detection, reduced exploratory drilling, and faster decision-making in upstream resource development.
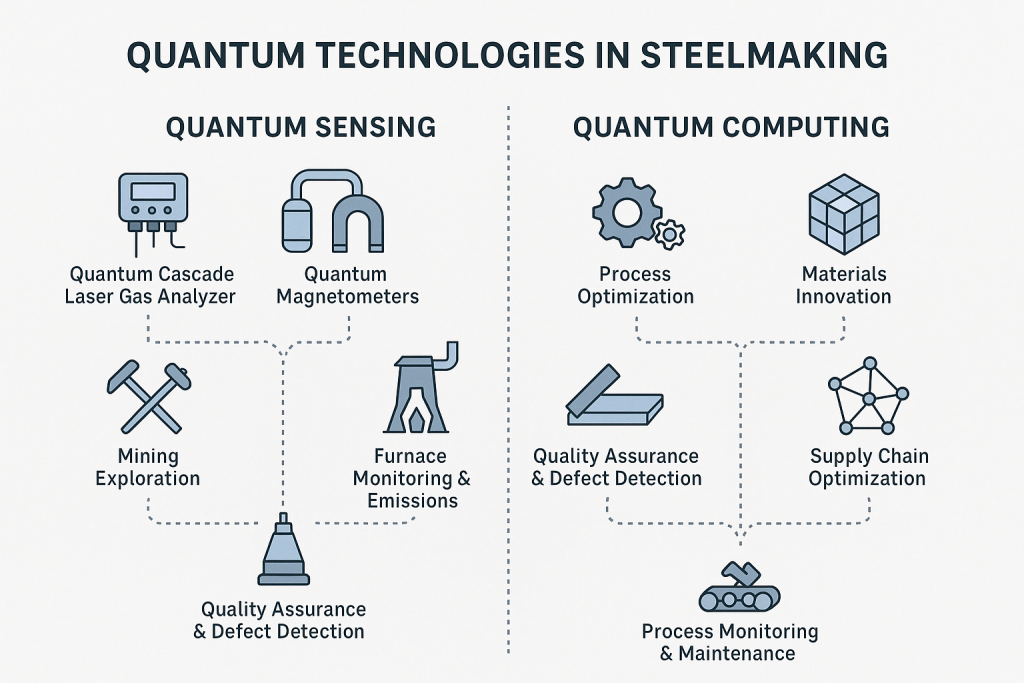
Quantum Computing: Optimization at Scale
Smarter Scheduling and Production
Nippon Steel has already piloted quantum computing for optimizing steel plant workflows. Using quantum algorithms, they simulated and solved intermediate production scheduling problems that are hard to address classically. The result: higher throughput, better inventory control, and reduced energy use.
Quantum AI for Blast Furnace Control
POSCO, one of the world’s largest steelmakers, is working with Terra Quantum to implement quantum neural networks in furnace operation. The goal is to optimize thermal and gas input to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions—going beyond what traditional AI can manage.
Alloy Design with Quantum Simulation
Quantum simulation allows modeling the atomic interactions in iron-carbon alloys, accelerating new steel grade development. Nippon Steel and Quantinuum recently simulated phase transformations in infinite iron lattices—an impossible task for classical computers—showing how quantum chemistry could revolutionize metallurgy.
Supply Chain Optimization
Steel production involves a vast logistics network. Quantum solvers are being tested for routing materials, coordinating deliveries, and minimizing emissions across global supply chains. Early pilots in this area have shown improvements in cost-efficiency and carbon footprint management.

